

Inflation is a popular topic of conversation in today’s society. This keyword is frequently discussed because of the impactful role it plays in most industries but what does it really mean?
It is the increased price of products and services over time also resulting in a decline of purchasing power, meaning the number of products and services you can purchase with your money decreases over time.
Whilst it causes an increase in the price of day-to-day necessities such as petrol and electricity, inflation is not all bad. For example, in the real estate market the value of property increases during times of high inflation causing a spike in rent charges.
What effect does inflation have on banks?
Central banks across the globe will increase their interest rates in order to counter inflation and encourage savings as with higher rates loans will become more expensive.
When debt is costlier it can influence consumer demand for goods and services, as well as business investments. This can help to reduce the effects of inflation as demand outweighs supply.
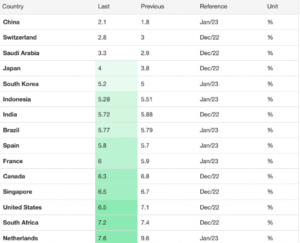
Whether it’s positive or negative, inflation is a reality that each industry has to come to terms with. It’s also important to take note of how inflation varies from country to country (as shown below).
What is deflation?
Deflation is a decrease in the price of goods and services in an economy over time. This means that the purchasing power increases, as the same amount of money can buy more goods and services than before.
Many economists have an everlasting fear of delation and most people are curious why. Firstly, if the prices fall so will consumer spending which is essential to a growing economy. Secondly, companies are likely to lay off workers due to slowed production rates ultimately leading to a decrease in the demand for products.